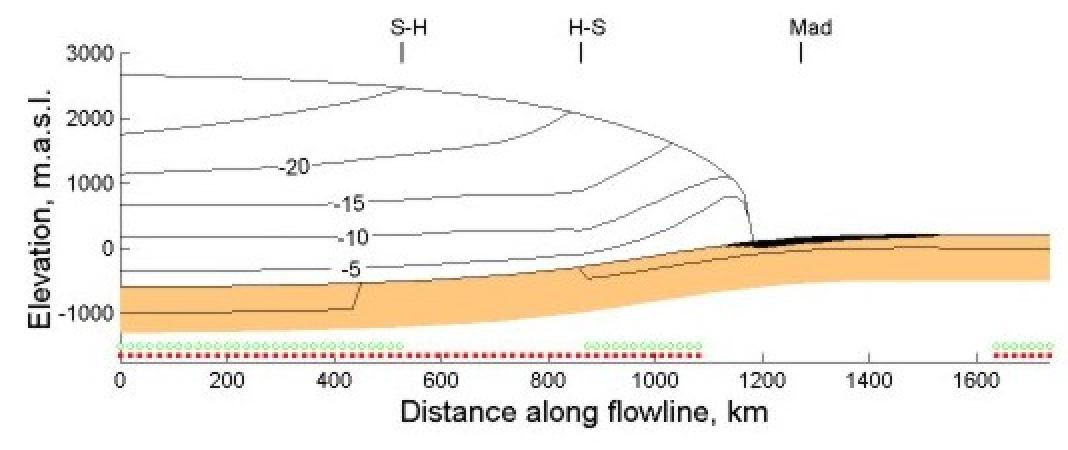
Ice sheet advancing over bedrock (orange) with permafrost (black)
Ice-Lobe permafrost interactions:

Influence of the Great Lakes:
The influence of deep water on the dynamics of LIS was studied. Lake
Superior induced iceberg calving rates that were sufficiently rapid to
delay ice advance across the deepest regions of the basin.
Consequently, ice failed to occupy the Driftless Area.
more...
Deglaciation of the southern Laurentide Ice Sheet:
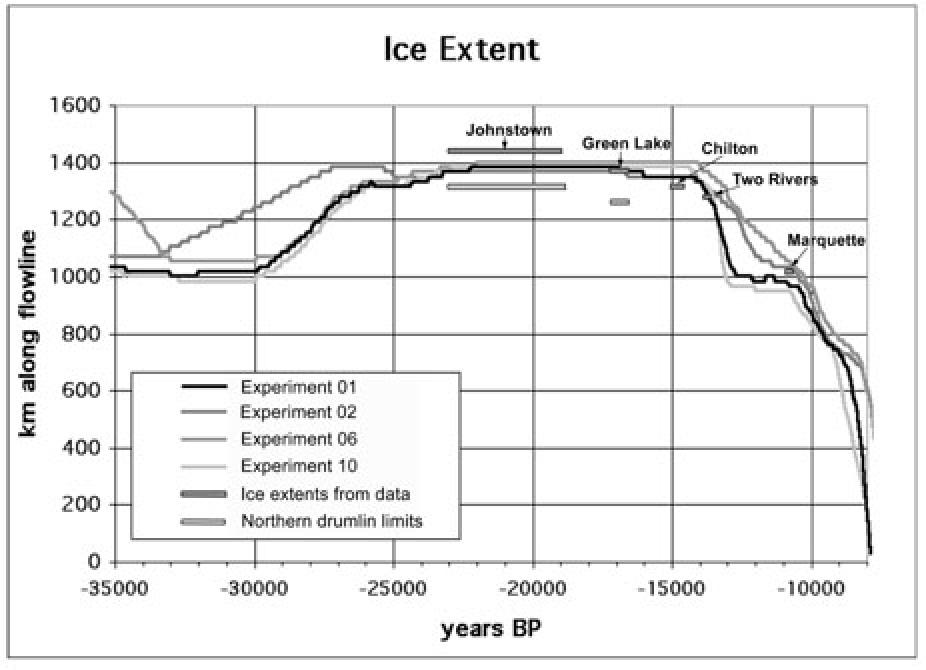
The deglaciation in the Green Bay lobe revealed clear evidence that
the extensive drumlin zones near the ice margins of the last glacial
maximum are associated with stagnant ice margins, high basal shear
stresses and extensive permafrost.
3-D model atempt
The thermodynamical coupled UBC ice sheet model is used to study
permafrost distribution underneath the ice sheet in order to
investigate the influence on the ice sheet's dynamical behaviour and
the conditions allowing formation of the observed landforms.